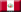| Designation: | ZSU-23-4 Shilka-M |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer: | Minotor-Service Unitary Enterprise | |
| Product type: | Armoured Vehicles | |
| Name: | Anti-aircraft system |
Close-in air defense (AD) systems play special role among field air defense weapons. Their primary task is to provide air defense of motorized and tank units and subunits in maneuvering combat and on the march by delivering fire on the move. Besides, practical close-in fighting requires that the systems be outfitted with effective AD guns capable of engaging both air and ground targets. The most successful type of these weapon systems is Russia’s famous Shilka self-propelled AD gun mount developed in the early 1960s and designed to fight primarily tactical aircraft and helicopters. The advent of tactical precision-guided weapons (PGW) called for the introduction of a missile channel to fight aircraft and helicopters before they could fire PGW. As a consequence, the renowned Tunguska AD gun-missile system was developed by the Tula Instrument Design Bureau and built in the 1980s.
Shilka SP gun mount
The intense development of air attack weapons has changed the approach to the modernization of this class of AD weapons. According to experts, the modernization potentialities of such systems as the Shilka and Tunguska have not yet been exhausted and optimal updating can considerably extend their service life, while their combat effectiveness canl satisfy the present-day requirements.
The principal lines of modernization of these systems are described below.
ZSU-23-4 Shilka Self-Propelled Air Defense Gun Mount
The modernization seeks for state-of-the-art design and technologies to update the self-propelled (SP) air defense gun mounts and make them effective in heavy electronic countermeasures (ECM) environments, in adverse weather and dust-laden conditions, in any season and at any time of day or night. The modernization envisages:
1. Integration of the modernized Shilka gun mounts into a unified army information system of air target reconnaissance and designation by organically assigning a mobile air target reconnaissance and control post (MRCP), Sborka, to the battery as its command post (BCP).
2. Improvement of the gun mount’s main part—the RPK-2 radar-computer complex (85 percent of the equipment accommodated in the turret) and creation of a new complex, the RPK-2U.
Battery command post:
Sborka MRCP
The radar has been virtually replaced by a new one, operating on the same frequency band but based on solid-state components: all units and systems of the radar have been subjected to modernization and the radar equipment is accommodated in five cabinets (instead of seven). The RPK-2U complex incorporates:
- digital computer system (DCS) which jointly with the radar makes up a fire control radar system (base system);
- television-aided sight and laser rangefinder which together with the radar and digital computer system form an optical-radar fire control system (ORFCS) operating in the passive mode both day and night (moonlight at a quarter of the moon);
- equipment, including:
(a) data receiving/transmitting (DRT) equipment for the gun mount to exchange information with the Sborka battery command post via a telecoded communication channel for reception of external target designation signals and operational control of the Shilka battery engaging a target by one, two, three and more gun mounts;
(b) digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital converters Ranzhir;
(c) trainer for radar operators;
(d) built-in equipment for check and adjustment of the RPK-2U complex low-frequency automatics and turret laying drives (2E2) in static and dynamic conditions;
(e) commander’s guidance unit (CGU).
3. Replacement of a number of systems, units and assemblies by up-to-date ones boasting higher technical and operating characteristics.
4. Updating of the base tracked vehicle and crew life support system.
The fire control radar system has been modified with the aim to:
- extend the air situation information field by integrating the gun mount into the unified field AD system;
- reduce the time of information processing in the fire control system (dead time);
- redistribute regular and random errors and pass bands of the follow-up systems and groups of the radar- computer complex systems;
- change the principle of introducing corrections for the angles of tilt and turn of the mount on the move;
- change the principle of error determination in the generation of total laying angles of the automatic guns;
- introduce and automatically account for meteorological data, corrections for changes in the muzzle velocity due to barrel bore wear, corrections in orientation and others (all refer to know-how);
- change the method of processing secondary information;
- modify some existing modes of battle performance.
The following innovations have been introduced:
- modes of operation to handle low-flying targets in heavy ECM environments (by the stored rate of range variation, stored target coordinates received from the digital computer system, moving target indication (MTI) by radar angular coordinates;
- automated control of the gun mount battle performance from a higher command post (HCP);
- built-in check of the electronic equipment;
- mode of radar operators’ training.
The above innovations have made it possible to:
- cosiderably enhance the air target search potential and acquisition probability;
- improve the radar immunity to passive jamming (with the introduction of angular automation channel protection and modernization of the MTI system range channel), active range deception jamming and tracking a jammer by angular coordinates (with the introduction of modes of tracking by the stored rate of target range variation and its inertial range and angle-aided tracking by signals from the digital computer system);
- provide the security of operation in heavy ECM environments (with the introduction of the optical-radar system);
- improve the precision characteristics of the follow-up systems and groups of the radar-computer complex systems;
- reduce the surveillance time of the fire control system.
The implementation of the above modifications has enhanced the effectiveness of fighting high-speed (up to 500 m/s) and small targets maneuvering at altitudes down to 25 m (0 m with the introduction of the ORS) rather than 100 m.
The air target (aircraft, helicopter) kill probability during one pass of the engagement zone at an ammunition expenditure of up to 300 rounds per gun mount constitutes 0.3 to 0.74 (rather than 0.07 to 0.12) and depends on the organization of control over the combat activity of the battery gun mounts from the higher command post and engagement of the target by one, two, three and more mounts. In addition to better technical characteristics, the operating characteristics have been also improved by providing:
- prompt functional check of the radar-computer complex and its components;
- means to upgrade training and practice of radar operators in handling air targets in heavy ECM environments without aircraft flights (up to five targets with simulation of operation under conditions of passive and noise jamming);
- better controllability and maneuverability of the tracked vehicle and reduced labor content required to maintain and operate the vehicle;
- higher reliability of starting the traction engine;
- better habitability conditions.
The service life of a modernized gun mount after the overhaul of non-modernized systems, units and assemblies has been extended, with spare parts being supplied.
The modernization of the Shilka SP gun mount changes the latter into a modern AD system which fits readily into training, repair and operating structures of clients and can provide cover of stationary installations, tank and motorized columns on the march in adverse weather and dust-laden conditions, in any season and at any time of day or night where other systems outfitted with optical guidance and control systems prove ineffective.
Tunguska-M1 Air Defense Gun-Missile System
Compared to the Tunguska-M, the Tunguska-M1 system ensures:
Tunguska-M1 SP mount
- automatic guidance of AD missiles (with manual correction for minor guidance deviations);
- automatic exchange of information with the battery command post (for higher efficiency of battery activity);
- batter immunity of the missile guidance channel (engagement of targets using optical decoys);
- engagement of small targets (cruise missiles of the ALCM type) owing to the use of a radar proximity target sensor (PTS) with circular radiation pattern;
- increase of the engagement zone within a range of 8 to 10 km.
Overall, the combat effectiveness of the Tunguska-M1 system in ECM environments is 1.3 to 1.5 times higher than that of the Tunguska-M system.
As compared to the 9M311 air defense missile, the 9M311-1M is noted for:
- installation of a radar proximity target sensor in place of the 8-beam laser one;
- installation of a pulsed light on the sustainer in place of the flare;
— increased operating time of the missile components which has allowed the firing range to be extended from 8 to 10 km.
The Tunguska-M system can be modernized by the manufacturing plant up to the Tunguska-M1 level.
The modernization package for the series-produced Tunguska-M system includes:
1. Introduction of reception and automatically controlled external target designation equipment in the SP mount. The equipment is interfaced with the battery command post over a radio channel which allows automatic distribution of targets among the battery SP mounts from the Ranzhir battery command post and considerably enhances the system combat effectiveness to repel mass attacks.
2. Introduction of a relief circuit to significantly facilitate the gunner’s work in optical tracking of a moving air target as if it were a stationary one. This considerably reduces tracking errors, which is essential for engagement of a target by a missile as in this case the miss value should not exceed 5 m.
3. Improvement of the coordinate determination equipment due to the application of a new type missile outfitted with a pulsed light in addition to the source of continuous light. This innovation significantly enhances the immunity of the equipment to optical decoys and the kill probability of targets using optical decoys. The employment of the new missile extends the target engagement range up to 10,000 m.
4. Modified system for measurement of tilt, gradient and course angles to allow an appreciable reduction in the perturbing action on gyros which occurs during movement of the SP mount, reduce errors in measurement of tilt and course angles of the SP mount, enhance the automatic gun fire control loop stability and, consequently, the kill probability.
The Ulyanovsk Mechanical Plant, the leading producer of renowned and advanced close-in and medium-range air defense weapons, offers modernized versions of the Shilka and Tunguska-M systems.
These are our offers for your consideration. Should you accept them, you will acquire highly effective air defense systems to ensure your country’s national security.
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
Related Articles |
|
Self-Propelled Anti-Aircraft Weapon (31.01.2013) |
|
RUSSIAN TECHNOLOGIES AT DSEi'2007 (12.09.2007) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |